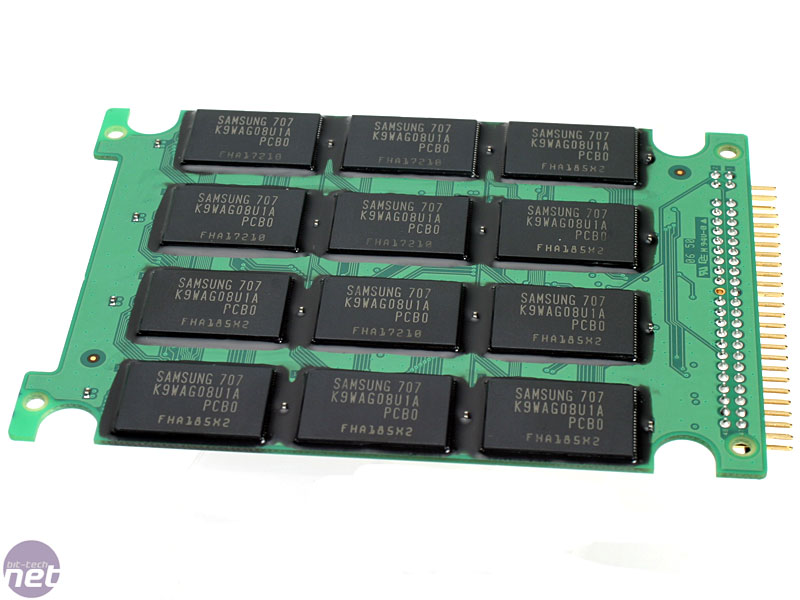
What Is Ssd Storage. Solid-state storage (sometimes abbreviated as SSS) is a type of non-volatile computer storage that stores and retrieves digital information using only electronic circuits, without any involvement of moving mechanical parts. A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory.

When you get down to a base level, an SSD is just some memory chips on a circuit board.
What is SSD Storage and What Are Its Benefits in Web Hosting?
In contrast to SSDs, HDD storage relies on spinning disks, motors, and read/write heads, using magnetism to store data on a rotating platter. Solid-state drives are SSDs come in a few different shapes and sizes, and that can affect their speed, their storage. A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/50537353/ssd-3d-nand-composite-form-factor-16x9.png.rendition.intel.web.720.405.0.0.png)

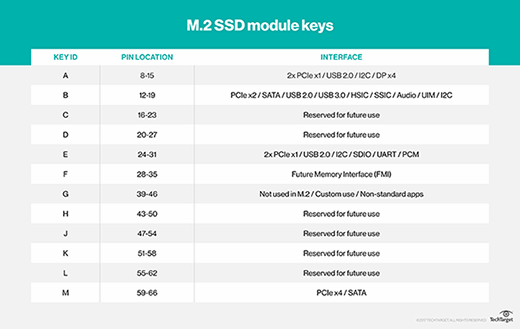





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SolidStateDrive_833448_final_2-b6dbce0b92e74a708eb33864a7c9ba35.png)